Your Guide To Living Well With Diabetes
July 28, 2021By: Amy Bennett
Categories: Diabetes, Live Healthy

When you have diabetes, your body either does not make or properly use insulin. Insulin is important. This is because it turns sugar, starches and other foods into the energy you need for daily life. Diabetes is a serious, lifelong condition. The good news is you can manage it and live well.
Types of Diabetes
Prediabetes is a warning sign. It usually develops before Type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes means your blood sugar is higher than normal. But, it's not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis. Lifestyle changes can often keep you from developing Type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults.This is because their bodies don’t produce insulin. Once known as juvenile diabetes. About 5% of people with diabetes have Type 1.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form. It develops when your body does not use insulin properly. It causes your blood sugar to rise to unhealthy levels.
Diabetes during pregnancy is also called gestational diabetes. It causes your blood sugar to rise to levels that can affect your pregnancy and your baby’s health. Your blood sugar usually returns to normal soon after delivery.
Manage Your Diabetes Successfully
- Exercise 30 minutes a day, five days a week.
- Get a wellness checkup once each year.
- Lose excess weight.
- Check your blood sugar regularly.
- Quit smoking.
- Take medicine as prescribed.
- Work with a dietitian on meal planning.
Recommended Targets
The American Diabetes Association recommends these targets for nonpregnant adults.
| Blood Glucose | General Goal | Keep In Mind |
|---|---|---|
| A1C | Less than 7% | The general goal of less than 7% is reasonable for most adults with diabetes. |
| Before meal | 80-130 mg/dL | |
| After meal | Less than 180 mg/dL | Measure your post-meal glucose 1-2 hours after the beginning of the meal. |
Symptoms
Hyperglycemia
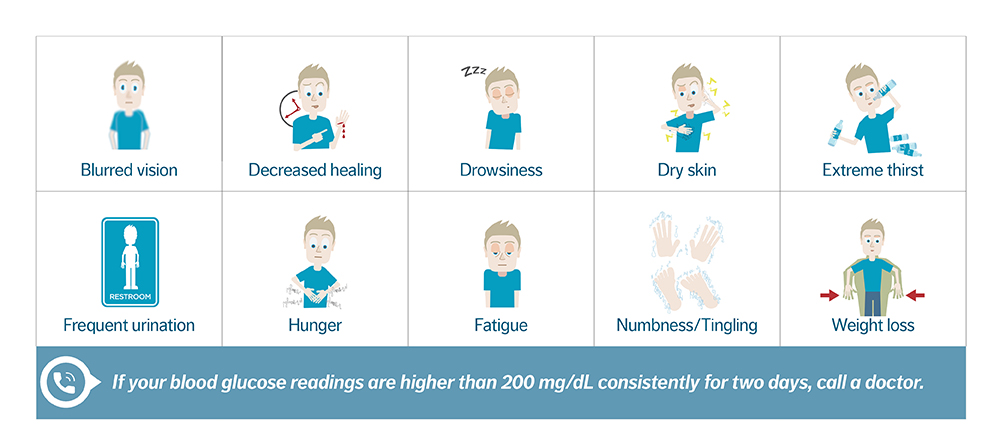
Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) comes on gradually and, if left untreated, can result in severe complications. It can be caused by certain foods and lack of physical activity, illness, some medications, or skipping or not taking enough diabetes medication.
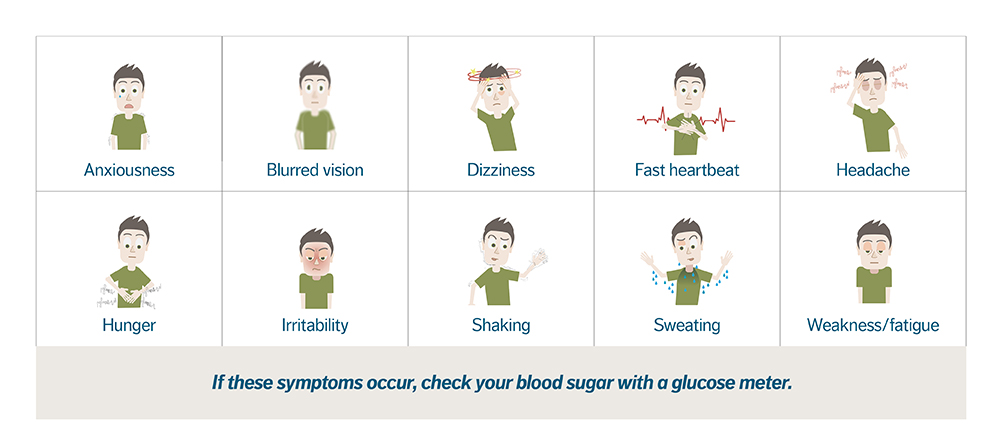
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is caused when a diabetic doesn’t have enough sugar (glucose) in their blood (usually when blood sugars fall below
70 mg/dL). It can occur suddenly and requires urgent treatment. Left untreated, it may lead to coma or even death.
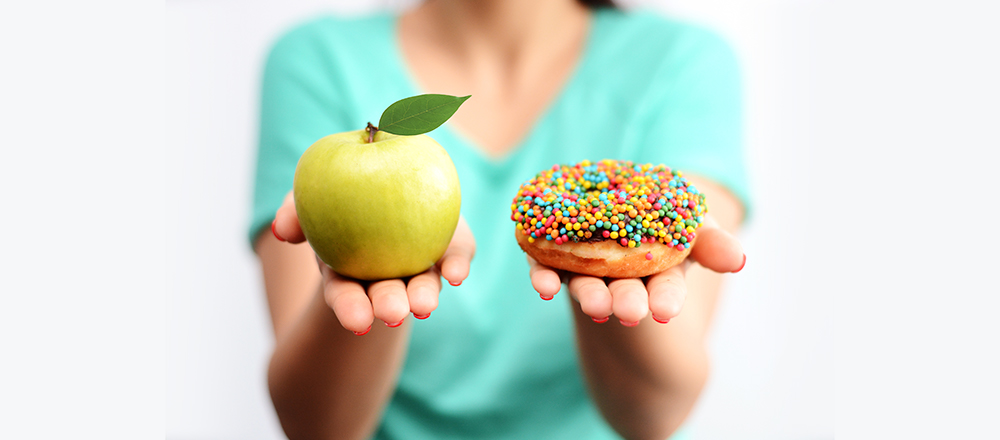
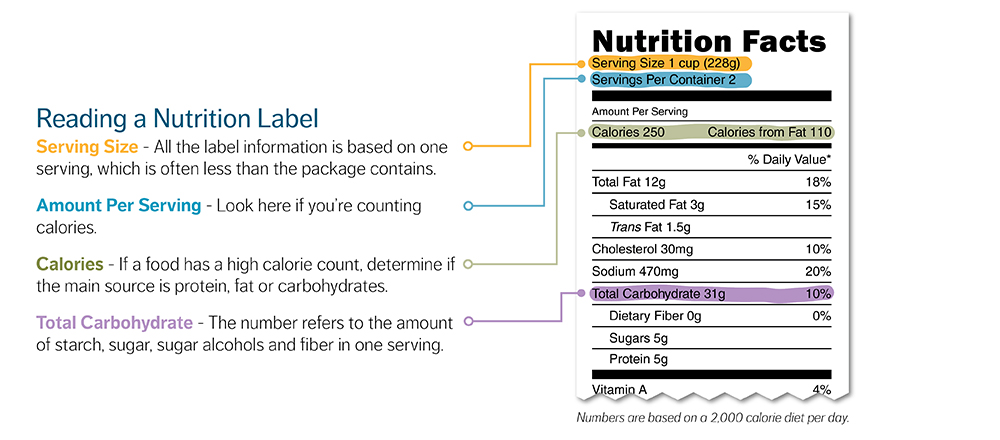
Healthy Eating
Healthy eating is one of the most important tools for managing diabetes.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates (carbs) are one of the body’s main sources of energy. By eating the right blend of carbs, the body will stay fueled and blood sugar can be better managed.
Complex Carbs
Because complex carbs are high in fiber, they slowly digest. Complex carbs stabilize blood sugar and allow the body to stay energized.
Try adding more of these complex carbs:
- Beans
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Whole grain pasta, breads and cereal
Simple Carbs
Simple carbs may cause blood sugar to spike.
Limit processed foods that contain simple carbs such as:
- Dessert
- Juice
- Potato chips
- Soda
- White breads, pasta and cereal
Fiber
Soluble fiber helps slow the body’s absorption of sugar, which can improve blood sugar levels.
Add more fiber by eating:
- Two to three servings of fruit every day*
- Three to six servings of vegetables every day**
*One serving of fruit = a small piece of fruit
**One serving of vegetables = 1 cup raw or cooked vegetables, or 2 cups raw, leafy greens
Fats
Choosing the right fats is key to healthy eating with diabetes.
Do:
- Choose foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids such as tuna, salmon, flax seed and walnuts.
- Choose monosaturated fats such as nuts, seeds, and olive, canola and peanut oils.
- Avoid saturated fats, which are in foods such as high-fat red meats and whole-fat dairy.
- Limit high-fat oils such as coconut and palm oil.
Physical and Mental Health
Exercise
Staying active can:
- Decrease stress levels
- Help the body use insulin better
- Help with weight management
- Improve heart health
- Lower blood sugar
- Reduce the need for diabetes medication
Tips:
- Check blood sugar levels before and after exercise.
- Choose an enjoyable activity.
- Take extra care of feet, and notify care team of any foot injuries.
- Wear a medical identification bracelet or necklace.
Try to get 30 minutes of moderate exercise at least five days a week. Also work on resistance exercises two to three times a week.
Remember to check with a doctor before starting any new exercise or activity.
Mental Health
Mental health is always important. It's especially important for those who have diabetes. The reason? Stress can raise blood sugar levels.
Manage stress by::
- Exercising
- Listening to music
- Meditating
- Spending time with family and friends
- Taking a break
Talk With Your Doctor
Your doctor is one of the best resources for help with living successfully with diabetes. If you need a physician, visit a list of our providers.
Nutrition Counseling
Find out about our outpatient nutrition counseling services by calling 816.691.5267. Most insurance plans reimburse for this type of service, but please check with your carrier in advance. To connect with a physician, visit a list of our providers.
Related Reading
Diabetes: Living the Sweet Life (Patient Story)